Pre Writing Skills – Why are they important?
Pre writing skills are necessary to master in the early years for many important reasons. Just like children need to walk before they can run, students need to master prewriting skills before they can have legible and efficient handwriting.

What are Pre Writing Skills?
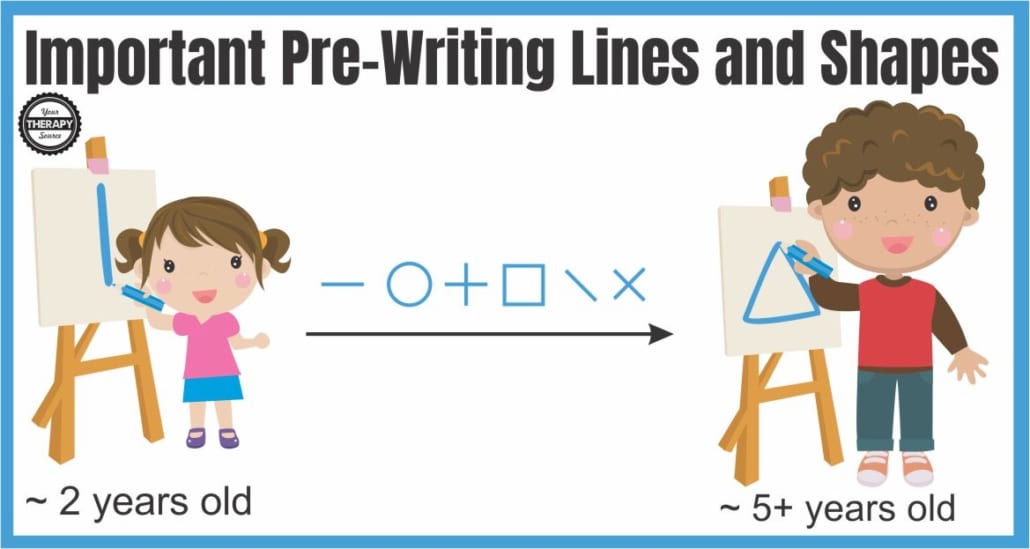
Pre writing skills or handwriting readiness involves practicing writing different shapes and fine motor skill development. Children move along a progression of learning how to make marks on paper. At first, children begin to scribble on paper. Then children learn to make marks on paper along a timeline starting at around 2 years of age.
Pre Writing Strokes
Here are the pre writing strokes in progression.
- scribbling
- vertical lines
- horizontal lines
- circle
- plus sign
- square
- diagonal lines
- X
- triangle (about 5 years+)
In addition to the pencil control required for pre writing activities like lines and shapes, children also need:
- adequate muscle strength in the fingers and hands
- postural control to remain upright while doing seat work
- visual motor integration skills – this is the ability to interpret visual information and respond with a motor action. For example, you see a baseball and you respond by moving your hands to catch the baseball. Research indicates that visual motor skills are related to academic performance and eye-hand coordination skills.
- attention span and focus
- visual perceptual skills to determine the size and shape
- bilateral coordination (one hand to write and one hand to hold the paper) – is the ability to use the right and left sides of the body together at the same time or with alternating movements.
- efficient pencil grasp – you can download visuals for proper pencil grip here
- object manipulation – this is the ability to pick up and use an object with one hand.
- motivation
- motor planning
- cognitive awareness of the task
Why are Pre Writing Skills Important?
Pre writing skills are the building blocks for efficient handwriting. Research indicates the following:
- early fine motor writing skills are an important school readiness skill associated with later academic success.
- writing by hand in the early years helps to support the development of reading skills.
- kindergartner’s visual-motor integration skills predict achievement in reading, math, writing and spelling.
In This Age of Technology Why Do We Need Pre Writing Activities and Handwriting?
You may wonder why do we even need these skills if we are such a
- teachers give higher grades to assignments produced with more attractive writing and that
are “easy to read” rather than those produced with less attractive writing. - difficulties with handwriting may influence the writer’s attention, requiring them to focus more on the writing and less on the thought process of what to write.
- children with handwriting difficulties may develop negative experiences of writing, including frustration, decreased self-efficacy,
and poor motivation. - handwriting requires fine motor control and fine motor activities stimulate the prefrontal cortex (part of the brain that helps with self-regulation and executive function).
What Can You Do to Help Children Develop Pre Writing Skills?
There are many activities that can help children develop pre-writing skills. It is important to remember to encourage children to play and interact with
Here are a few suggestions to help children develop pre-writing skills:
- fine motor skill practice: lacing beads, play dough, interlocking building blocks, finger games, craft projects, buttoning, and more.
- free time to scribble, draw and interact with pencil and paper.
- working on a vertical surface
- pencil and paper pre-writing tasks
Resources for Pre Writing Skills

The Prewriting Bundle includes all 11 digital downloads to provide prewriting practice for early writers. Start students on the right path to form good writing habits prior to letter formation or use to practice the skills necessary for legible handwriting.
Reference: Dinehart, L. H. (2015). Handwriting in early childhood education: Current research and future implications. Journal of Early Childhood Literacy, 15(1), 97-118.
Download a PDF Copy of this Article
You can download a FREE PDF copy of this article here.



